Search:
Page Number:
Sunny Rays and AnglesSkills Reference 2 Skills you Will Use
Safety
Caution Use caution when working around bulb, it will be very hot when turned on. Protect your hand with gloves when necessary. Be careful when using sharp scissors. In the ray model of light, light is represented as straight lines called rays. These light rays carry and transfer energy, which is why light rays from the Sun warm the Earth and surfaces of objects on Earth. The amount of energy transferred and warming depends on the angle at which light rays strike objects or the Earth. QuestionHow do light rays transfer energy to objects when striking them at different angles? Materials and Equipment
Dry LabA "dry lab" activity includes collected data for your convenience. If you wish to perform this lab and collect your own data, use the following procedure. ProcedurePlease watch the following video for procedure steps 1 through 9. The procedure is also provided in text in the downloads at the bottom of this page. Analyzing and Interpreting
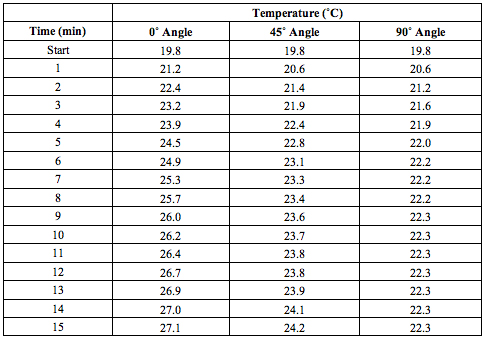
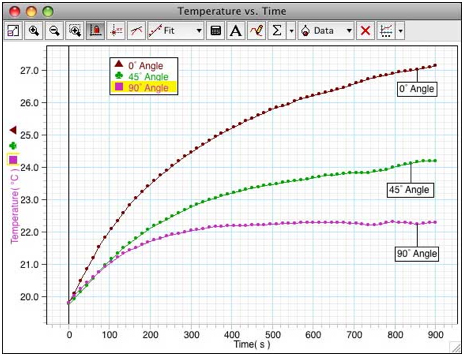
Forming Conclusions
|